Virtual machine management has never been easier for SCTG’s Managed VMware Cloud. Here’s how the upgraded new interface affects virtual machine management and administration.
Virtual machine management tools now faster from the Actions menu
Immediately upon logging in, you will be taken to the virtual machine management homescreen:
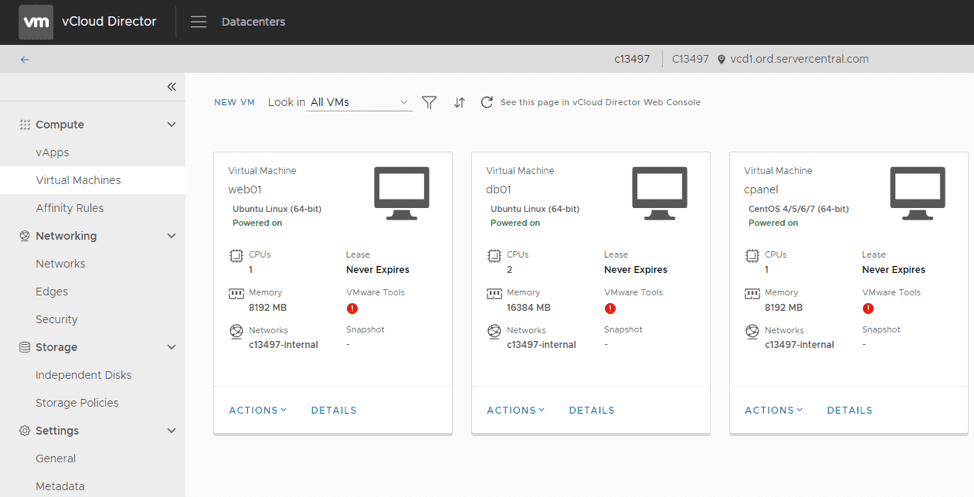
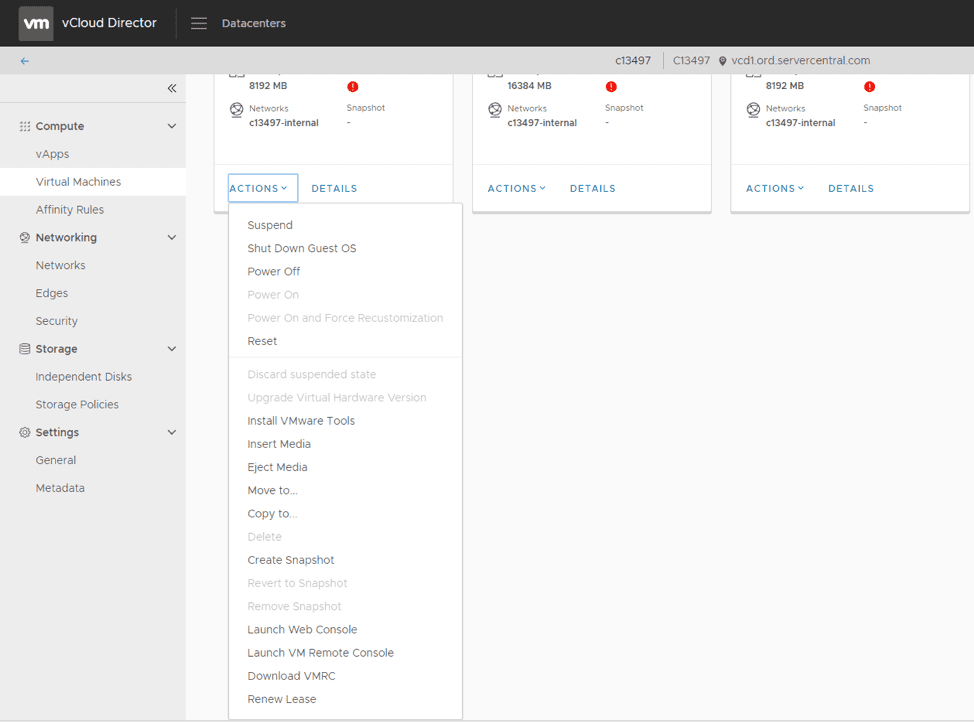
To manage a virtual machine, click the Actions dropdown menu. Here, you can start, stop, install VMware tools, insert media, create snapshots, and more:
Launching Web Console and virtual machine management
The console of each virtual machine can be accessed by clicking on the VM’s computer monitor icon or by selecting Launch Web Console or Launch VM Remote Console in the Actions dropdown menu:
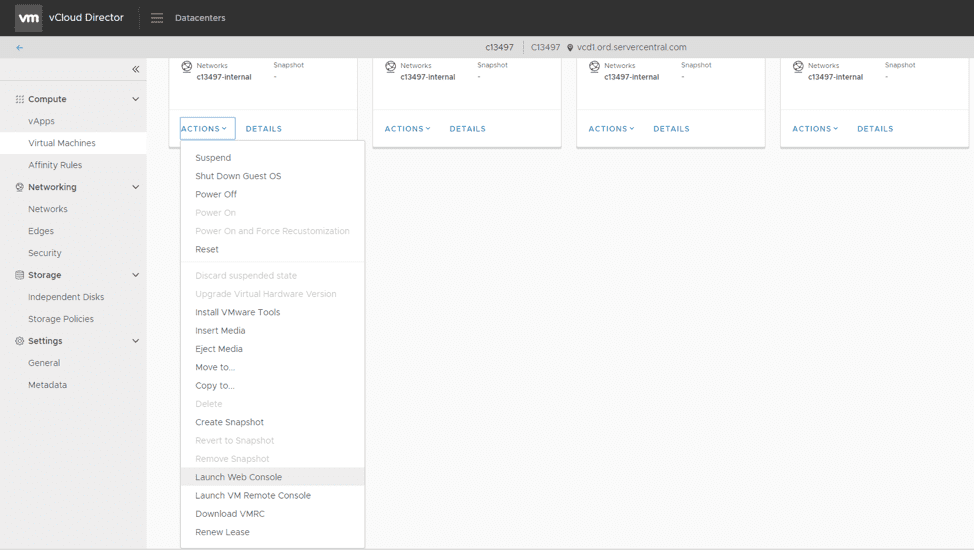
You may need to download the VMRC plugin if you use VMRC.
Check out our Managed VMware Cloud vCloud director upgrade
Creating virtual machines
Among many of the standard virtual machine management features available in the new Managed VMware Cloud UI is the ability to create and delete virtual machines.
Once you’re logged in, click the New VM button located at the top of the page. This brings up a one-page window to define the new VM’s configuration:
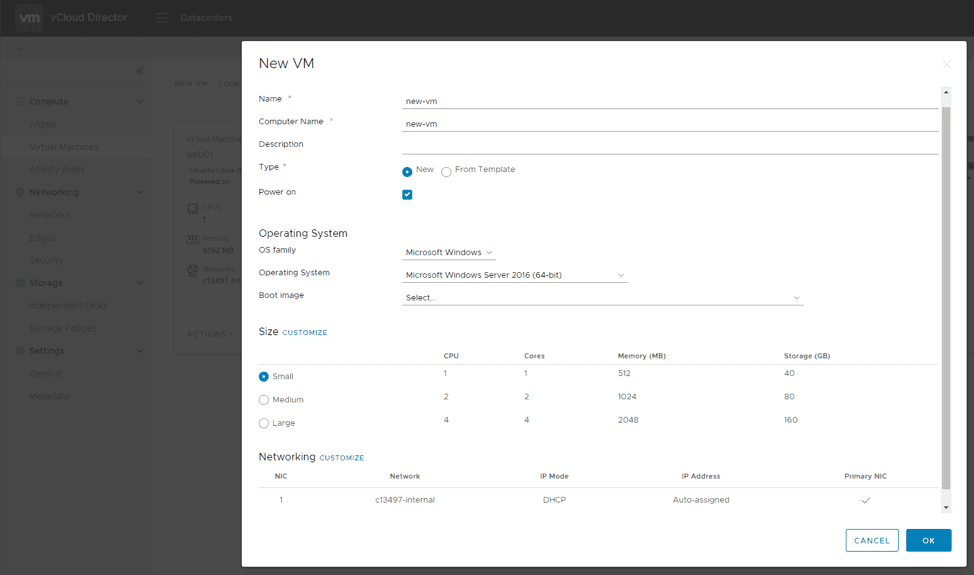
Here, you can give the virtual machine a name, deploy from scratch or an available template, define the architecture and operating system, and select the proper media to deploy with (if not using a template):
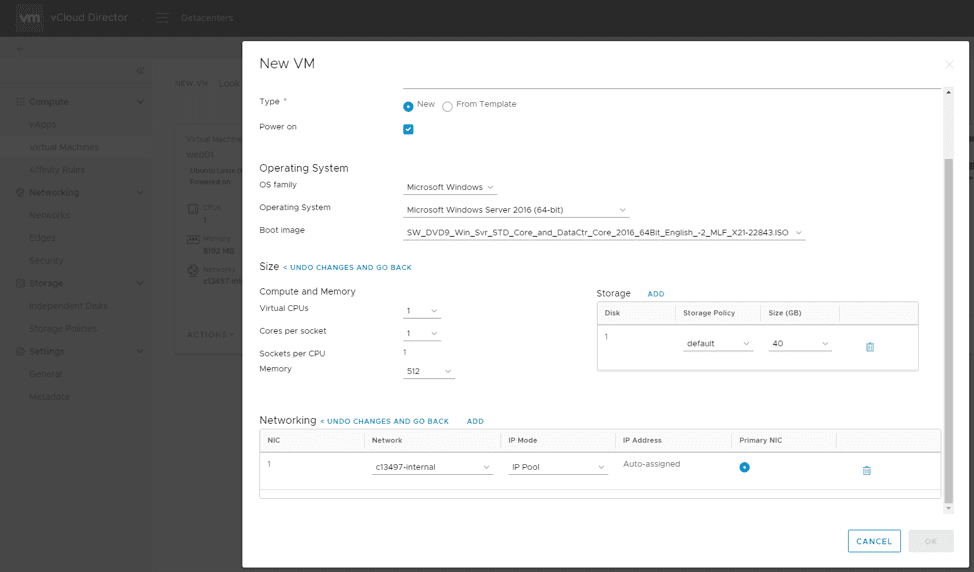
Hardware parameters such as the size of the virtual machine can be customized to your exact specifications, including networking and storage. Typically, Managed VMware Cloud customers have at least one internal network to use which is NAT’d through an Edge Gateway. We’ll expand on that in another post.
See how we brought the Managed VMware Cloud to financial powerhouse Verito
It’s important that the proper configuration is selected for networking to work as expected. When building a new virtual machine from scratch, be sure to customize your configuration. Networking should use IP Pool instead of DHCP, unless your environment is set up to support it or other networking configurations have been provided.
Once the configuration is finalized, the virtual machine will begin its creation and power on sequence. If any media was attached or a template was used, it will boot into these as needed. From there, you can configure the operating system just as you would for a traditional server.
Virtual machine management services: Deleting VMs
To delete a virtual machine, go to the VM’s Actions menu and select Delete. Simple!
Turning VMs off and on
Virtual machines can also be turned on or off as needed through the Actions menu.
Creating snapshots
Snapshots are useful for creating a restore point before doing a major update or change. Snapshots can be taken or deleted at any time via a VM’s Actions menu. Each virtual machine can have one customer-created snapshot at a time.
Set VM parameters and configuration from the Details link
Click the Details link on a VM to change its configuration and parameters:
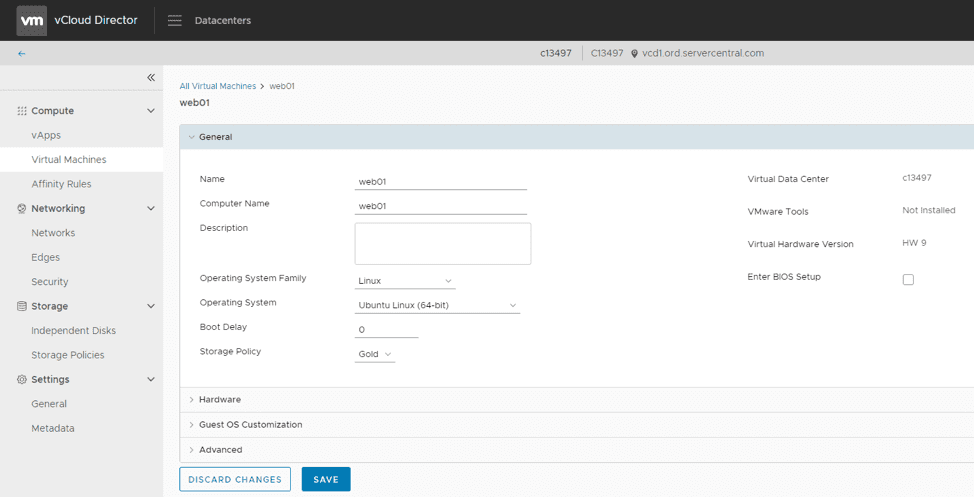
Details > General
The first section under Details is General. This controls standard information – things like virtual machine name, boot configuration, and specifying the architecture and guest operating system.
It’s important to note that the architecture/guest operating system parameters do not affect the operating system running on the virtual machine. Instead, these parameters allow VMware to identify the guest operating system and provide certain background configurations for compatibility purposes.
Details > Hardware
The second section under Details is Hardware. This provides a means to modify the hardware configuration of the virtual machine – things like changing the vCPU, memory, storage, and network configuration.
Note: Adding certain resources may require shutting down a virtual machine before it hardware can be added. For example, if adding additional vCPUs or memory, the virtual machine will need to be shut down unless Memory Hot Add or Virtual CPU Hot Add are enabled.
Tip: We recommend disabling Hot Add to avoid performance and resource management issues. Windows, for example, will not use the new memory or CPU for already-running applications (and requires a reboot to do so).
Storage and network parameters can be changed here as well, so more disks/disk space and additional network adapters can be added as needed:
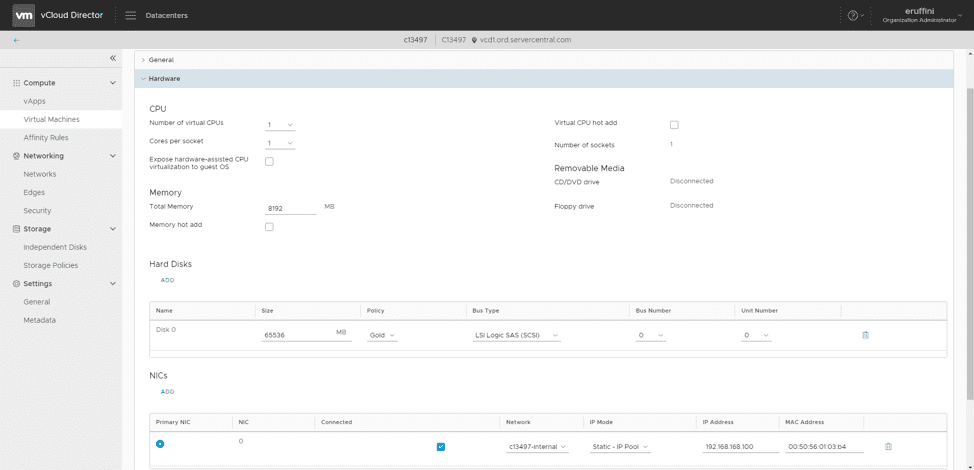
The hardware available to you depends on the contracted resources within your Managed VMware Cloud contract. You can always add more resources by contacting your sales representative.
Details > Guest OS Customization
Managed VMware Cloud users can now do custom OS deployments and templating in the Guest OS Customization section. This area allows you to deploy a guest operating system and customize the operating system as it’s deployed:
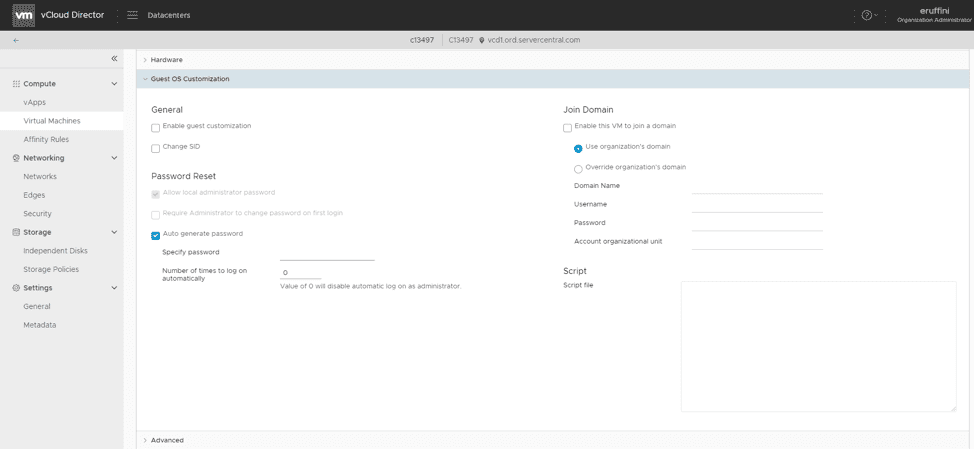
This feature is primarily geared towards Windows, but we can help you with guest OS customization for Linux-based operating systems as needed.
Details > Advanced
The Advanced section page provides the ability to configure reservations and limits to virtual machine resource utilization within your Managed VMware Cloud environment. It also allows metadata to be added for organizational purposes.
Resource shares and reservations can be used to prevent virtual machines from consuming too many resources within your environment. They can also be used to ensure that critical virtual machines get the resources they require when running your applications.
